Each field sample in the field sample file reflects an underlying relation between soil and its relative environmental conditions, and this relation would recur over the space. It is assumed that locations with similar environmental conditions will have similar soil property/type. Therefore, each sample can be considered representative over locations with similar environmental conditions. That is, each sample has individual representativeness. Moreover, the representativeness level of an individual sample on an unsampled location can be approximated by the environmental similarity between them. Based on this concept, the soil property/type on unsampled locations can be predicted by referring to environmentally similar samples.
Before any inference can be done, similarity between each pixel and each field sample should firstly be estimated.
In SoLIM Solutions, similarity calculations are conducted at two levels: variable level and sample level.
Similarity Calculation at Variable Level:
The type of methods for calculating similarity on variable level depends on the type of the environmental variable.
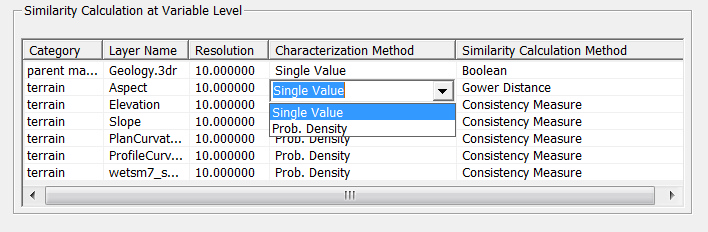
Single Value
If the variable is nominal or order, Boolean function should be used. For example, Boolean function is suitable for determing parent material similarity. That is, if the parent material of the pixel to be inferred and the field sample location are the same, the similarity value is 1, otherwise, the similarity value is 0.
If the variable is interval or ratio, Gower Distance can be used.
Both Boolean function and Gower Distance are single value similarity calculation methods.
Probability Density
If some layers have higher resolution, we can resample them into coarser resolution and use either Boolean or Gower Distance to calculate similarity. However, SoLIM Solutions provides another alternative to handle this case: using probability density estimation and consistency measurement. That is, with one coarser pixel, a probability density function (curve) is estimated to characterize environmental variable with higher resolution, then a Consistency Measure (CM) which quantifies the consistency between two curves, was introduced to measure the similarity.
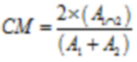
where ![]() ,
,![]() are the areas under probability distribution curve1 and curve2, while
are the areas under probability distribution curve1 and curve2, while![]() is the area under both curves. If curve1 and curve2 are the same, the CM will be 1; if curve1 and curve2 have no overlap, the CM will be 0.
is the area under both curves. If curve1 and curve2 are the same, the CM will be 1; if curve1 and curve2 have no overlap, the CM will be 0.
You can choose variable level similarity calculation method for each environmental variable. Note that for different types of environmental variable, there are different default settings (e.g. for parent material layer, Single Value - Boolean function are the default).
SoLIM Solutions uses the minimum similarity within one category as the final similarity of this category. For example, if there are 5 climate layers, the calculated similarities between one pixel and one field sample point using the 5 layers are 0.9, 0.6, 0.8, 0.7 and 0.9 respectively. The final climate similarity between the pixel and the field sample is 0.6 since it's the minimum among the five.
Similarity Calculation at Sample Level:
Similarity calculation at sample level, in fact, is integrating similarities at variable level. SoLIM Solutions provides three integration methods:
Limiting Factor
It assumes that the least favorite environmental condition determines soil property on a given site, so the minimum similarity among the five environmental categories is used as the final similarity. This is the default method.
Weighted-Average
If each environment category has same significance, this integration method can be used.
User Defined
If this method id selected, users can customize weights of different environmental variables.
Users can select different method from the drop-down list.

Once similarity calculation methods are determined, inference can be conducted. Inference methods for soil property and soil type are different.
Soil Property Inference and Uncertainty Quantification:
Then soil property of each pixel is predicted by integrating the soil property values at sample points using the calculated similarities as weights.
Besides soil property prediction, the predicting uncertainty can also be quantified. Predicting uncertainty on an unsampled location would be high if there are no samples environmentally similar with this location. That is to say, if similarities with all samples are all very low, the uncertainty of the soil property at certain pixel will be high.
It should be noted that for one pixel, if the uncertainty is higher than the uncertainty threshold, the soil property will be set to NoData.
Soil Type Inference:
For certain soil type, all the field samples which have that soil type are selected and the environmental similarity between a pixel and selected sampled location are measured. Then the maximum similarity is assigned to the pixel for the soil type. Therefore, the final results are a set of similarity files, one for each soil type.