The directory in which SoLIM Solutions 2013 is installed is referred to as <SoLIM Solutions installed directory>. The data sets needed for the tutorial should have been installed in a directory named "Tutorial_Data" under <SoLIM Solutions installed directory>.
After starting SoLIM Solutions 2013 you will see the following user interface:
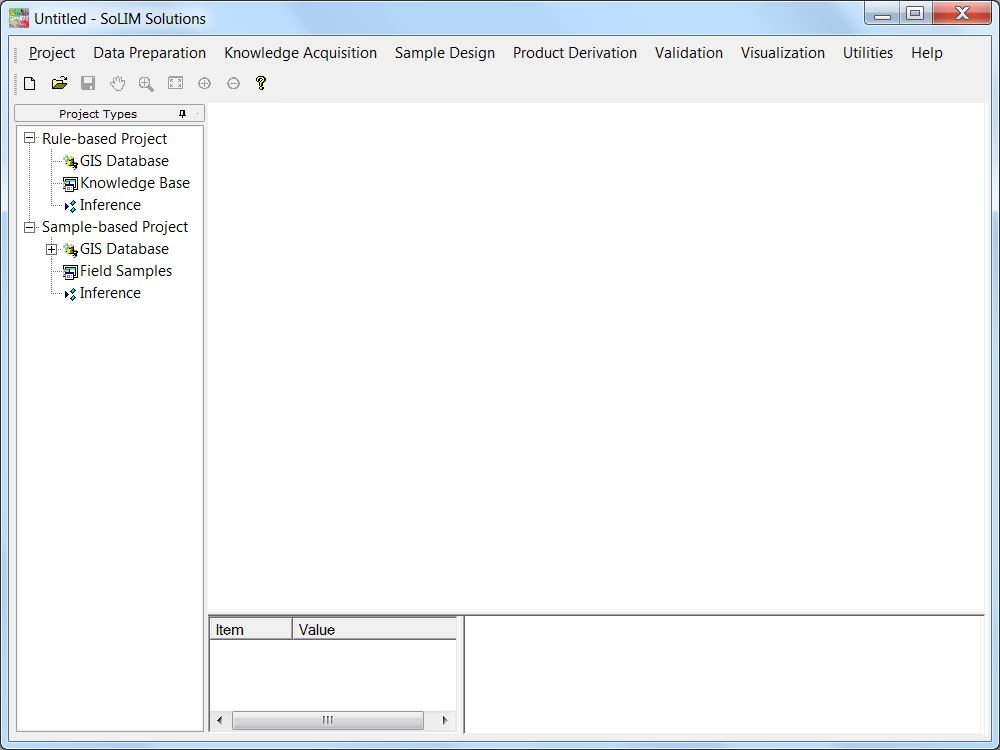
The Menu:
![]()
The "Project" menu provides the interface for managing the projects. A project maintains all necessary information needed for performing a SoLIM inference (soil mapping). Project menu also supports importing existing projects created with the old versions of SoLIM software.
The "Data Preparation" menu provides terrain analysis tools which implement the most recently developed ideas in digital terrain analysis and it also provides tools for extracting soil-related surface dynamic feedback from remote sensing data (Zhu et al., 2013).
The "Knowledge Acquisition" menu provides tools to extract knowledge from experts or through purposive sampling.
The "Sample Design" menu provides traditional sample design tools as well as purposive sampling design tool.
The "Production Derivation" menu provides the interface to produce soil type maps (hardened maps) and soil property maps derived using fuzzy soil membership maps.
The "Validation" menu provides tools to evaluate the results (type maps and property maps) using field point data.
The "Visualization" menu provides tools to visualize environmental data layer and inference results in 2D or 3D form.
The "Utilities" menu provides file conversion and other data analysis utilities.
The Toolbar:
![]()
The toolbar provides some frequently-used functions, including creating project, saving project and exploring environmental data layers.
The Project Panel:
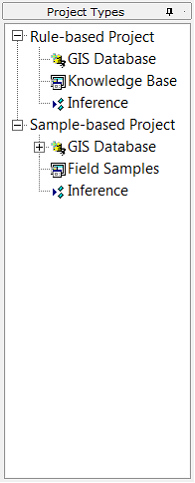
The project panel contains a tree-style list. It is used to control SoLIM projects.
As you can see from this panel, SoLIM Solutions 2013 supports two types of projects: rule-based and sample-based. Both rule-based project and sample-based project are based on the idea that soil types and/or soil properties can be inferred from soil-related environmental conditions, so they both require a set of GIS layers (GIS Database) which depict the soil-related environmental conditions. The difference between them is that in rule-base project, we need to define a set of rules (Knowledge Base) to express the soil-environment relationship explicitly, while in sample-base project, we just need to provide field sample points (Field Samples). As stated before the sample-based project does not need the samples based on any spatial sampling design. You will have a better understanding of the difference after you go through this tutorial. Currently, the two projects cannot be mixed.
Views:
The view area is for displaying current information based on the node selected in the project panel. The figure above shows the view for GIS database management.