Select "Data Preparation->Surface Derivative". Specify the parameters, the algorithms and the output file.
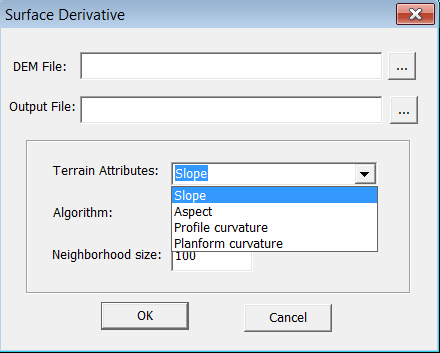
Output: Slope
Gradient (result is in percent (tan(degree)))
Output: Aspect
The orientation of the line of steepest descent (Result is in degree)
Output: Profile curvature
Slope profile curvature
Output: Planform curvature
Contour curvature
DEM file
The DEM data of the area.
Neighborhood size
The size of the neighborhood.
You can select different algorithms to do this. Three algorithms are available: Evans-Young, Horn, Zevenhergen-Thorn.
Algorithm: Evans-Young's (Evans, 1972; Young, 1978; Evans, 1979)
The essence of the Evans–Young method consists of the following parts: The non-smooth land surface in the vicinity of a given point is replaced by a "sheet" of a smooth surface (the second-order polynomial) that is fitted to the real surface by a least squares criterion. After that, this smooth surface ("sheet") is used for calculations of MVs that are expressed by first and second partial derivatives.
Algorithm: Horn's
Algorithm used by ArcInfo. It uses square-shape neighborhood. When using circular neighbor, this method becomes equivalent to Evans' (1972).
Algorithm: Zevenbergen-Thorne's (Zevenbergen and Thorne, 1987)